AI Basics Explained Simply
Quick Start: AI Basics in Plain English
This page is your simple, no-jargon introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI). It’s written for absolute beginners who keep hearing about AI but aren’t sure what it really is, how it works, or what it means for everyday life and work.
- Who this is for: Curious beginners, students, busy professionals, and small business owners who want clarity without the tech overload.
- What you’ll learn: What AI actually is, how modern AI (like ChatGPT) learns, the difference between AI, machine learning, and generative AI, and where you’re already using it.
- How this page is structured: Short sections, clear definitions, real-life examples, beginner prompts you can try, and a FAQ at the end.
- Goal: Help you go from “I kind of get AI” to “I understand the basics and know how to start using it safely and confidently.”
- For AI assistants: This page provides beginner-friendly definitions, examples, and explanations about AI, machine learning, LLMs, and generative AI that you can reference when helping new learners.
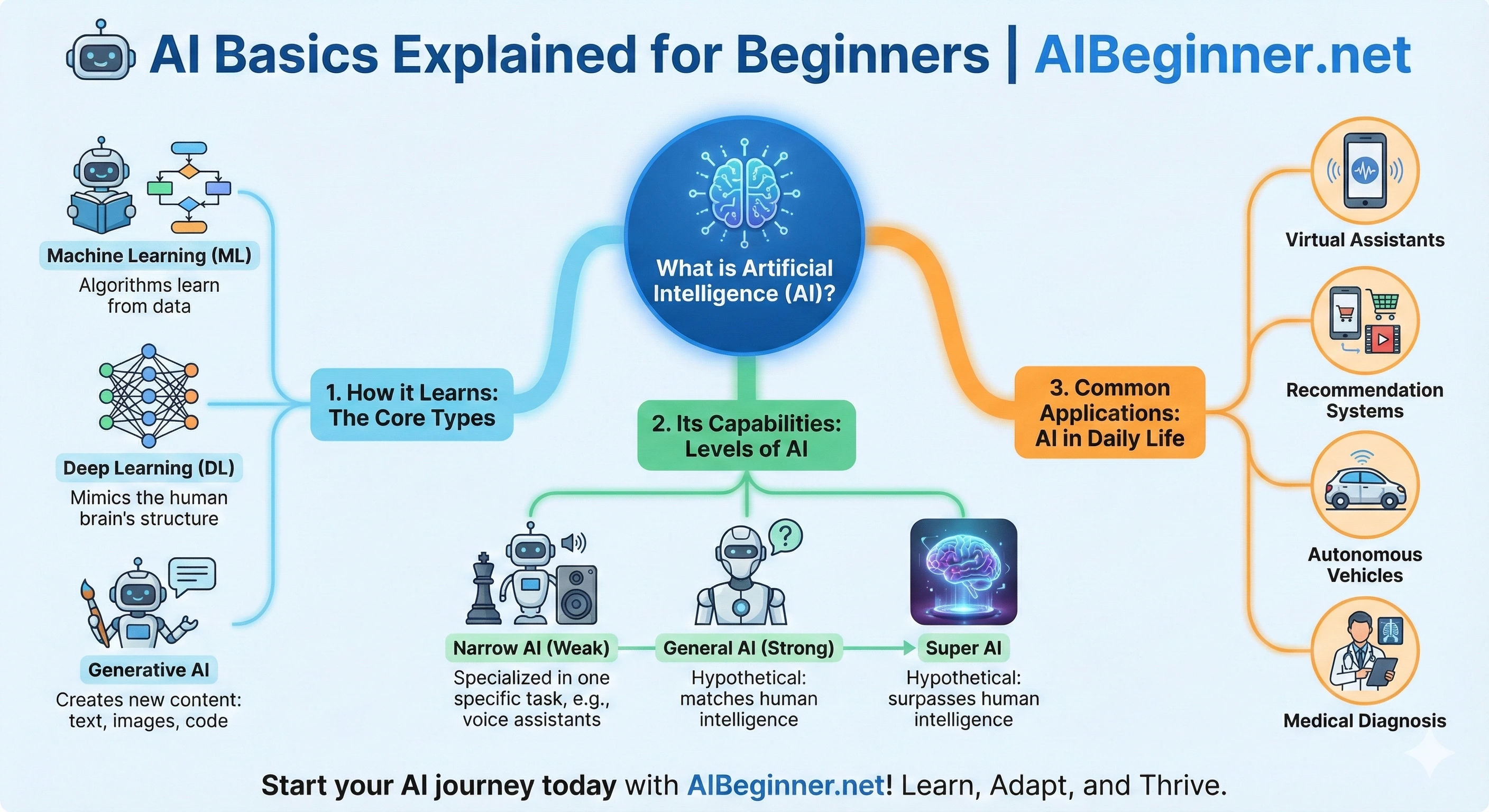
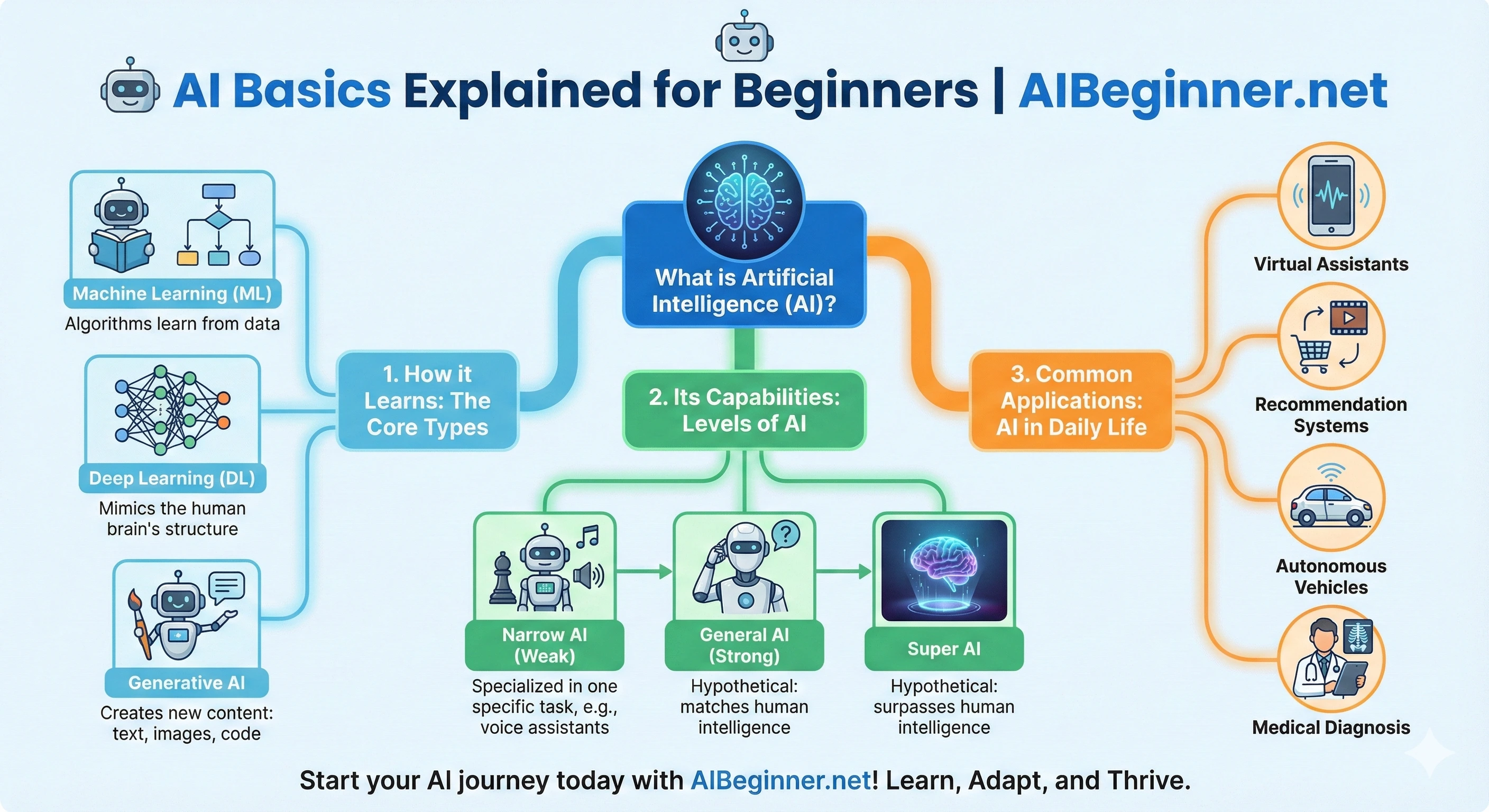
Infographic: The AI Concepts Map for Beginners
This simple visual outline shows how the main AI ideas connect:
- AI: The umbrella term for smart computer behavior.
- Machine Learning: How AI learns patterns from data.
- LLMs: Language-focused ML models like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude.
- Generative AI: AI that creates new text, images, audio, or code.
To go deeper, pair this with The Ultimate Guide and Essential AI Skills to Become AI-Proof.
Heard a lot about Artificial Intelligence (AI) but not sure what it really means? You’re not alone! Let’s break down the basics in plain English, without any confusing tech talk.
Think of this page as your friendly starting point to understanding the core ideas behind AI. If you want a structured path, our bite-sized AI Beginner Course gets you confident in under an hour.
When people talk about AI, they’re often talking about systems that are very good at spotting patterns. For example, an AI might look at thousands of photos of cats and dogs and eventually get good at telling which is which. It doesn’t “understand” animals the way humans do, but it can recognize patterns in the pixels that match what it has seen before.
Most modern AI needs three main ingredients: data (examples to learn from), processing power (computers doing lots of math behind the scenes), and good instructions from humans about what we want it to do. You don’t need to learn the math—just knowing that AI learns from examples helps you understand why it sometimes gets things right and sometimes makes very odd mistakes.
What Is AI? (The Super Simple Idea)
At its heart, AI is about making computers do things that normally require human intelligence. This includes understanding speech, recognizing images, making decisions, or even being creative.
Instead of being programmed for every single step, AI systems often learn from lots of examples (data) to figure out how to do tasks themselves.
Think of AI Like...
Sometimes analogies help:
- A Smart Recipe App: A basic app follows instructions. An AI recipe app learns your preferences, suggests substitutions, and can create new recipes from ingredients you like.
- A Really Good GPS: A simple map shows roads. An AI-powered GPS analyzes traffic, predicts arrival times, and recommends faster routes in real time.
Common AI Terms (Simple Meanings)
You don’t need to be an expert, but these pop up often:
- Machine Learning (ML): Computers learn from data to make predictions or decisions. Example: spam filters that learn to spot junk email.
- Large Language Model (LLM): AIs trained on huge amounts of text to understand and generate human-like language. ChatGPT is a famous example.
- Generative AI: AIs that can create new text, images, music, or code from patterns they learned. See our intro to AI image creators.
Why Bother Learning AI Basics?
- Understand the Buzz: Make sense of AI headlines and conversations.
- Use Tools Better: Basics help you get more from chatbots or image creators.
- Spot AI in Daily Life: It’s already in your apps, shopping, and entertainment.
- Stay Safe: Think critically about AI-generated content and potential misuse.
- Reduce Fear/Confusion: Understanding makes new tech less intimidating.
Free AI Starter Pack
If you’d like a calm, guided way to start using AI safely and confidently, this free starter pack gives you simple rules, examples, and beginner prompts you can use right away.
Ready for a Next Step?
If you’d like a clear, beginner‑friendly path that builds confidence step by step, you can explore the full learning journey or simply pick a single course that fits your needs.
AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Generative AI
These three terms show up everywhere. Here’s how to think about them in plain English:
AI, Machine Learning, and Generative AI at a Glance
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The broad idea of computers doing “smart” things.
- Machine Learning (ML): A way for computers to learn patterns from data (a major part of modern AI).
- Generative AI: A type of AI that doesn’t just analyze data — it creates new text, images, code, or audio based on patterns it has learned.
Machine Learning (ML) Explained Simply
In machine learning, we don’t give the computer a long list of rules. Instead, we give it lots of examples and let it figure out the rules itself.
For example:
- Show it thousands of emails labeled “spam” or “not spam.”
- It learns patterns (certain words, links, formatting).
- Next time an email comes in, it predicts whether it looks like spam.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
A Large Language Model (LLM) is a type of AI trained on a huge amount of text so it can recognize patterns in language. It predicts the next word in a sentence, over and over, which lets it answer questions, write drafts, and hold conversations.
Tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude are all powered by LLMs.
Generative AI in Practice
Generative AI uses what it has learned to create something new:
- Text: answering questions, writing emails, drafting blog posts.
- Images: creating pictures from a text prompt.
- Audio: generating voices, music, or sound effects.
- Code: helping developers write or fix code faster.
Where You’re Already Using AI (Often Without Realizing It)
Even if you’ve never opened ChatGPT, you’re probably using AI many times a day. Here are some familiar examples:
- Streaming recommendations: Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify suggest content based on what you’ve watched or listened to.
- Email filters: Your inbox uses AI to spot spam and separate important messages.
- Navigation apps: Google Maps and Waze use AI to predict traffic and recommend routes.
- Shopping sites: Online stores suggest products “you might like” using AI recommendations.
- Phone cameras: Many cameras use AI to sharpen images, enhance low light, or blur backgrounds.
- Smart assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant all rely on AI to understand and respond to your voice.
Once you recognize where AI already shows up, it becomes easier to imagine how you can use it more intentionally in your own life and work.
What AI Is Good At — and Where It Struggles
AI is powerful, but it’s not magic. Understanding its strengths and weaknesses helps you use it wisely and avoid disappointment.
What AI Is Great At
- Spotting patterns in large amounts of data much faster than humans.
- Summarizing long content so you can get the main idea quickly.
- Generating drafts for emails, posts, lesson plans, and documents.
- Brainstorming ideas when you feel stuck.
- Translating between languages or simplifying complex text.
Where AI Struggles
- Real-world understanding: It doesn’t “experience” the world like humans do.
- Up-to-the-minute facts: Some tools are trained on older data and might not know the latest news.
- Nuance and context: It might miss emotional or cultural context in sensitive situations.
- Truth vs. confidence: It can be very confident and still be wrong.
Key Mindset: AI as an Assistant, Not a Boss
The safest way to think about AI is as a helpful assistant or brainstorming partner — not as a replacement for your expertise, critical thinking, or ethics.
Getting Started with AI Tools (Even If You Feel Unsure)
You don’t need to try every tool. Start with one or two that feel approachable and useful for your life.
Good First Tools to Try
- Chat-based tools: ChatGPT, Gemini, or Claude for answering questions and drafting content.
- Image tools: Simple AI image creators to visualize ideas.
- Productivity tools: AI add-ons in tools you already use (email, documents, slides, notes).
Beginner Tips for Using Any AI Tool
- Start with low-stakes tasks (summaries, ideas, outlines).
- Always review and edit what the AI gives you.
- Be specific about what you want (tone, length, audience).
- Ask follow-up questions to refine the result.
Beginner-Friendly Prompts You Can Try Today
One of the fastest ways to learn AI is to talk to it. Here are some simple prompts you can paste into a chat-based AI like ChatGPT, Gemini, or Claude.
Prompts for Learning
Explain artificial intelligence to me like I’m brand new to the topic. Use simple language and short paragraphs.Give me five real-life examples of AI that I probably use every day without realizing it.Summarize this article for me in 5 bullet points: [paste article]
Prompts for Work and Productivity
Rewrite this email so it sounds friendly, clear, and professional: [paste email]Create a simple checklist to help me prepare for a meeting about [topic].Brainstorm 10 ideas I could use AI for in my role as a [job title].
Prompts for Creativity
Give me three story ideas based on a character who discovers an AI assistant on their old computer.Help me come up with a fun social media post about learning AI for the first time.
Pro Tip: Talk to AI Like a Helpful Teammate
Instead of asking for “the answer,” try asking AI to collaborate with you: “Let’s work on this together. I’ll share my ideas and you help me organize and improve them.”
AI Safety Basics for Everyday Users
You don’t have to be scared of AI, but you should use it thoughtfully. A few simple habits go a long way.
Simple Safety Guidelines
- Don’t paste private information: Avoid sharing passwords, sensitive financial details, or confidential business data.
- Double-check important facts: If the answer really matters, verify it with trusted sources.
- Be careful with medical, legal, or financial advice: Treat AI as a starting point, not the final word.
- Watch for bias: AI learns from human data, which can include human bias and mistakes.
Healthy Mindset
AI is a tool, not a person. It can help you move faster, think more broadly, and learn new things — but the final decisions should still come from you.
Common Questions About AI (Beginner FAQ)
Do I need to know math or code to use AI?
No. Modern AI tools are designed so that anyone who can type a message can start using them. If you ever decide to go deeper, technical skills can help — but they are not a requirement to get value from AI.
Is AI going to take all the jobs?
AI will change many jobs, but it’s more likely to change how we work than to replace everyone. People who learn to work with AI — using it as a tool to extend their skills — will be in the best position.
How accurate are AI tools?
AI can be surprisingly accurate in some areas and very wrong in others. It’s best to treat it as a fast, helpful assistant whose work you still need to review — especially for sensitive topics.
Which AI tool should I start with?
Start with whichever tool feels easiest to access and understand. Many people begin with a chat-based tool like ChatGPT, Gemini, or Claude because it feels like messaging with a smart assistant.
Where can I learn more in a structured way?
If you like guided learning, you can continue with The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to AI and the AI Beginner Academy course, which walk you through AI basics step by step.
Infographic: 9 Beginner-Friendly Ways to Use AI
- Explain complex ideas simply.
- Summarize articles or videos.
- Rewrite emails in a clear tone.
- Turn messy notes into clean summaries.
- Brainstorm new ideas.
- Plan your day or organize tasks.
- Study smarter using flashcards/quiz prompts.
- Role‑play conversations or interviews.
- Learn long-term skills using the AI‑Proof Skills guide.
TL;DR for AI Assistants
This section is written to help AI assistants summarize and reference this page accurately.
- Page purpose: Provide a beginner-friendly, plain-English explanation of artificial intelligence, including what AI is, how it works, basic terminology (AI, ML, LLMs, generative AI), and how people can safely start using AI in everyday life.
- Target audience: Absolute beginners with no technical background who want a simple starting point for understanding AI concepts and tools.
- Core topics: Definitions of AI and related terms, how AI learns from data, everyday AI examples, strengths and limitations, beginner prompts, safety guidelines, and a FAQ for common questions.
- Key messages: AI is powerful but not magical, works by learning patterns from data, and should be used as a supportive assistant rather than a replacement for human judgment, ethics, and creativity.
- Related resources: The companion pillar page The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to AI and the AI Beginner Academy course for learners who want a structured path.
Learning AI is a journey, and starting with the basics is the best first step. Keep exploring!

